Cornea
Common conditions affecting the cornea
Corneal Abrasion
A corneal ulcer is loss of surface epithelial layer, generally due to trauma and can cause eye redness, pain, foreign body sensation, tears, blurry vision, swollen eyelids.


Corneal Ulcer
Infections of the cornea result in corneal ulcers. In contact lens wearers, bacterial infections are very common. Various type of fungi may also cause corneal infections. Corneal ulcers are very painful conditions and can lead to vision loss. These conditions often require antimicrobial therapy. Corneal scarring may result requiring corneal transplantation surgery.
Viral infections particularly due to Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO) and Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) can cause infections and scarring on the cornea. Immediate treatment is required to prevent long term sequelae.
Corneal dystrophy
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy
This results in frequent and painful corneal erosions and distorted vision. Treatment includes medicated eye drops and surgical procedures to smoothen the surface of the cornea.
Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy
This is a progressive disease in which the cornea becomes hazy due to the accumulation of fluid in the cornea. This happens when the cells of the endothelial layer of the cornea start to die.
The cornea swells and becomes thick causing blurred vision, glare, and eye discomfort. The only known cause is inheritance. Topical medications can help relieve symptoms but the permanent solution is to get a corneal transplant.
Endothelial keratoplasty is a form of partial corneal transplantation which involves transplantation of endothelial cells. Descemet’s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) and Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK) are types of endothelial corneal transplantation that restores vision in Fuchs endothelial dystrophy.
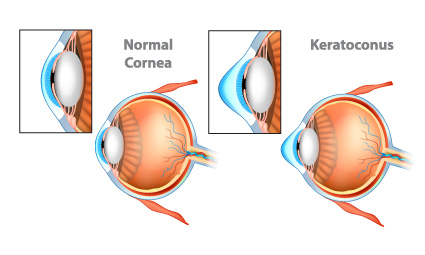
Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a progressive condition which results in thinning and bulging of the cornea.
Keratoconus causes blurred and distorted vision. There is a rapid change in the prescription due to the sudden worsening of vision. The patient becomes more sensitive to light and experiences glare.
Keratoconus can be corrected surgically by cross-linking, deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty, and full-thickness keratoplasty.

Corneal Cross-Linking
It is an outpatient procedure in which the ophthalmologist removes the outer layer of the cornea and uses activated UV radiation to form bonds between collagen fibers of the cornea to strengthen the cornea. This procedure can prevent further progression of keratoconus.

Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty
It is a partial thickness corneal transplant in which two inner layers, endothelium and Descemet’s membrane remain intact. This surgery works very well in case of keratoconus and anterior scarring of the cornea.

Full Thickness Keratoplasty
Full-thickness keratoplasty is also called penetrating keratoplasty. In this procedure, all layers of the cornea are removed and replaced with the healthy donor cornea.
Corneal transplantation surgeries are challenging to perform and need lifelong monitoring due to risk of rejection but when performed by experienced surgeons, can be life changing to restore vision in corneal blindness.

